Image via
As a beginner navigating the world of cannabis, you’ve probably heard about THC, CBD, and a variety of other cannabinoids. But have you heard of HHO, HHC, or HHC-O? In this article, we’ll break down what these terms mean, how HHO is made, and how they differ from more commonly known cannabinoids like Delta 9 and Delta 8.
What are HHC, HHO, and HHC-O?
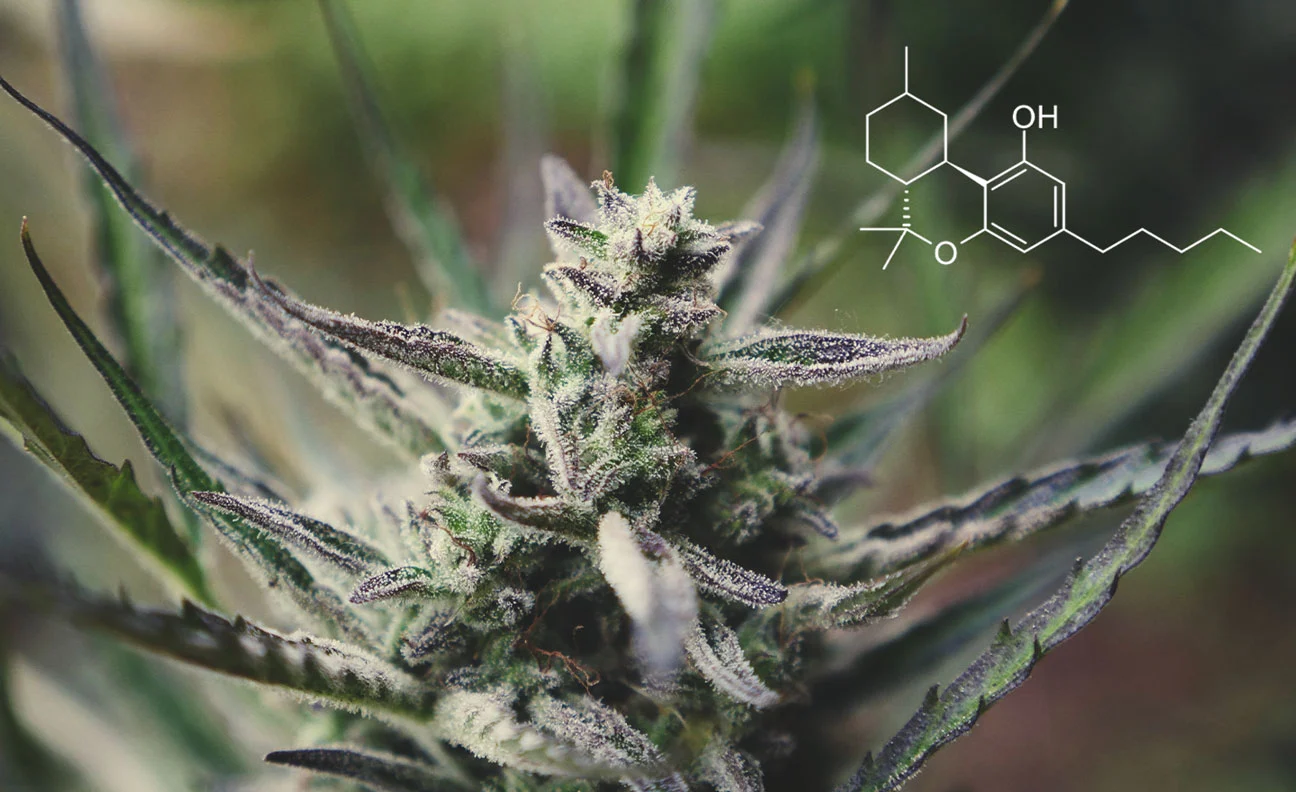
Firstly, let’s clarify: it’s “HHO,” not “HH0”. The world of cannabinoids is rife with acronyms, so let’s decode these lesser-known terms. HHO stands for Hexahydrocannabinol, HHC for Hydrogenated Cannabinol, and HHC-O for Hydrogenated Cannabinol-Oxide. These are all hydrogenated forms of existing cannabinoids, typically created in a lab setting to explore their unique properties and effects.
How is HHC and HHO Made?
Creating HHO involves a scientific process known as hydrogenation. Existing cannabinoids like THC or CBD undergo this process, which adds hydrogen atoms to their molecular structure. This modification often results in a compound with altered effects and characteristics.
While both HHC and HHO are hydrogenated cannabinoids, they differ in their origins and potential effects. HHC, or Hydrogenated Cannabinol, originates from CBD, whereas HHO, Hexahydrocannabinol, is derived from THC. Because they come from different parent cannabinoids, their effects can vary considerably. HHC is generally more focused on offering therapeutic benefits without intense psychoactive effects. HHO, on the other hand, does carry psychoactive properties but at a less intense level compared to its parent compound, THC. Both are created through the process of hydrogenation, but because of their different origins, they cater to different needs and experiences in the cannabis spectrum.
Steps to Make HHC:
Isolate CBD: First, pure CBD (Cannabidiol) is isolated from hemp or cannabis plants through an extraction process.
Prepare Reactor: The isolated CBD is then placed in a reactor, which is a specialized chamber where the chemical reaction will occur.
Introduce Catalyst: A catalyst, often a metal like palladium or nickel, is introduced to facilitate the hydrogenation process.
Add Hydrogen: Hydrogen gas is then injected into the reactor at a specified pressure and temperature.
Initiate Reaction: The catalyst helps break the double bonds in the CBD molecule, allowing hydrogen atoms to attach.
Monitor: The reaction is carefully monitored to ensure that it is proceeding as expected. This usually involves both time and temperature controls.
Stop Reaction: Once the desired level of hydrogenation is achieved, the reaction is stopped, often by lowering the temperature or by removing the catalyst.
Purify: The resulting mixture undergoes a purification process to isolate HHC from any remaining CBD and other byproducts.
Analyze: The final product is then analyzed using various methods like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) to ensure its purity and concentration.
Package: Once purity is confirmed, the HHC is ready to be formulated into various products like oils, tinctures, or edibles.
It’s crucial to note that the production of HHC should only be conducted by qualified professionals in a controlled environment to ensure safety and efficacy.
What’s Different from Delta 9?
Delta 9-THC is the most commonly known psychoactive component in cannabis. HHO and its counterparts are generally less psychoactive. Users report a milder, more balanced experience when consuming these hydrogenated forms.
How Does It Differ from Delta 8?
Delta 8-THC is an isomer of Delta 9, known for producing less intense psychoactive effects. Like Delta 8, HHO is also less intense than Delta 9 but could have some unique effects of its own that are still being studied.
Different from THC-O?
THC-O is another synthetic cannabinoid, but unlike HHO, it’s an acetate ester of THC. It’s far more potent than Delta 9-THC and comes with its own set of risks and effects, which differ significantly from those of HHO.
Can You Be Tested for HHO?
As of now, standard drug tests are not designed to detect HHO, HHC, or HHC-O. However, as these cannabinoids become more widespread, testing methods may evolve.
Is HHO Legal?
The legal status of HHO and other hydrogenated cannabinoids is a grey area and may vary by jurisdiction. In the United States, they are not explicitly listed as controlled substances but could be considered analogs to THC, depending on local laws.
Ultimately, HHO, HHC, and HHC-O offer a different range of experiences compared to more well-known cannabinoids. They’re still new to the scene, so exercise caution and consult local laws before diving in. With evolving science and potential legal changes on the horizon, these novel cannabinoids may offer exciting opportunities for both medical and recreational cannabis users.